For example, assume that the students are going to lease vans from their university’s motor pool to drive to their conference. A university van will hold eight passengers, at a cost of $200 per van. If they send one to eight participants, the fixed cost for the van would be $200. If they send nine to sixteen students, the fixed cost would be $400 because they will need two vans. We would consider the relevant range to be between one and eight passengers, and the fixed cost in this range would be $200.
Contribution Margin: What it is and How to Calculate it
However, the growing trend in many segments of the economy is to convert labor-intensive enterprises (primarily variable costs) to operations heavily dependent on equipment or technology (primarily fixed costs). For example, in retail, many functions that were previously performed by people are now performed by machines or software, such as the self-checkout counters in stores such as Walmart, Costco, and Lowe’s. Since machine and software costs are often depreciated or amortized, these costs tend to be the same or fixed, no matter the level of activity within a given relevant range. Contribution margin is the remaining earnings that have not been taken up by variable costs and that can be used to cover fixed costs. Profit is any money left over after all variable and fixed costs have been settled.
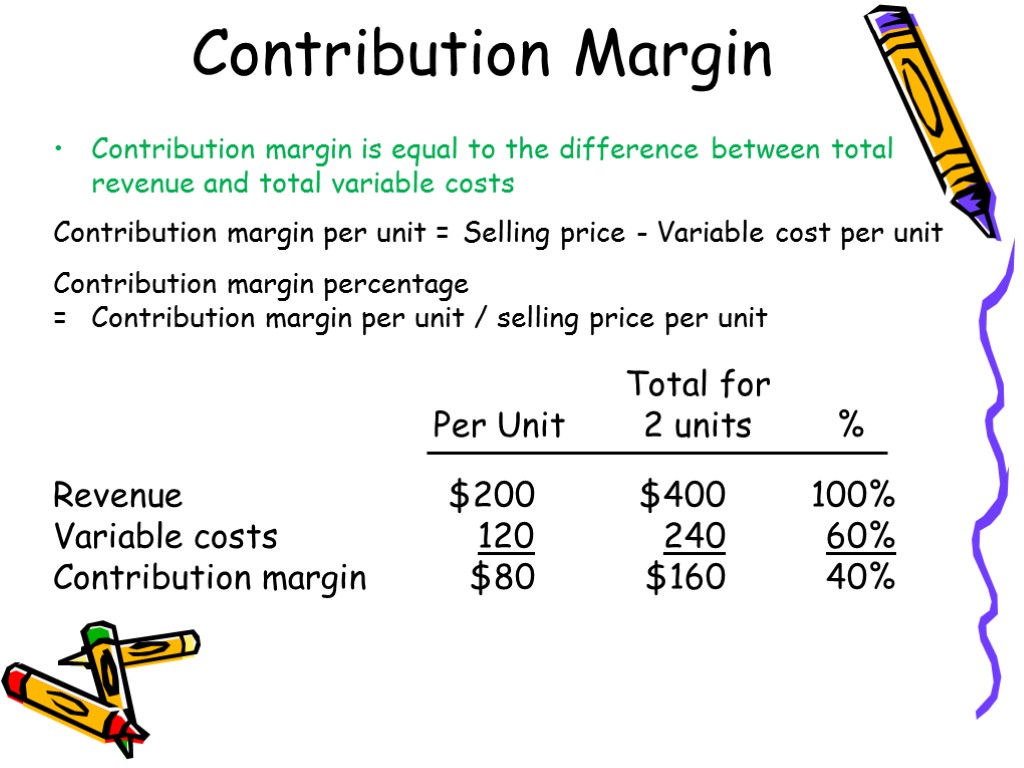
Contribution Margin for Overall Business in Dollars
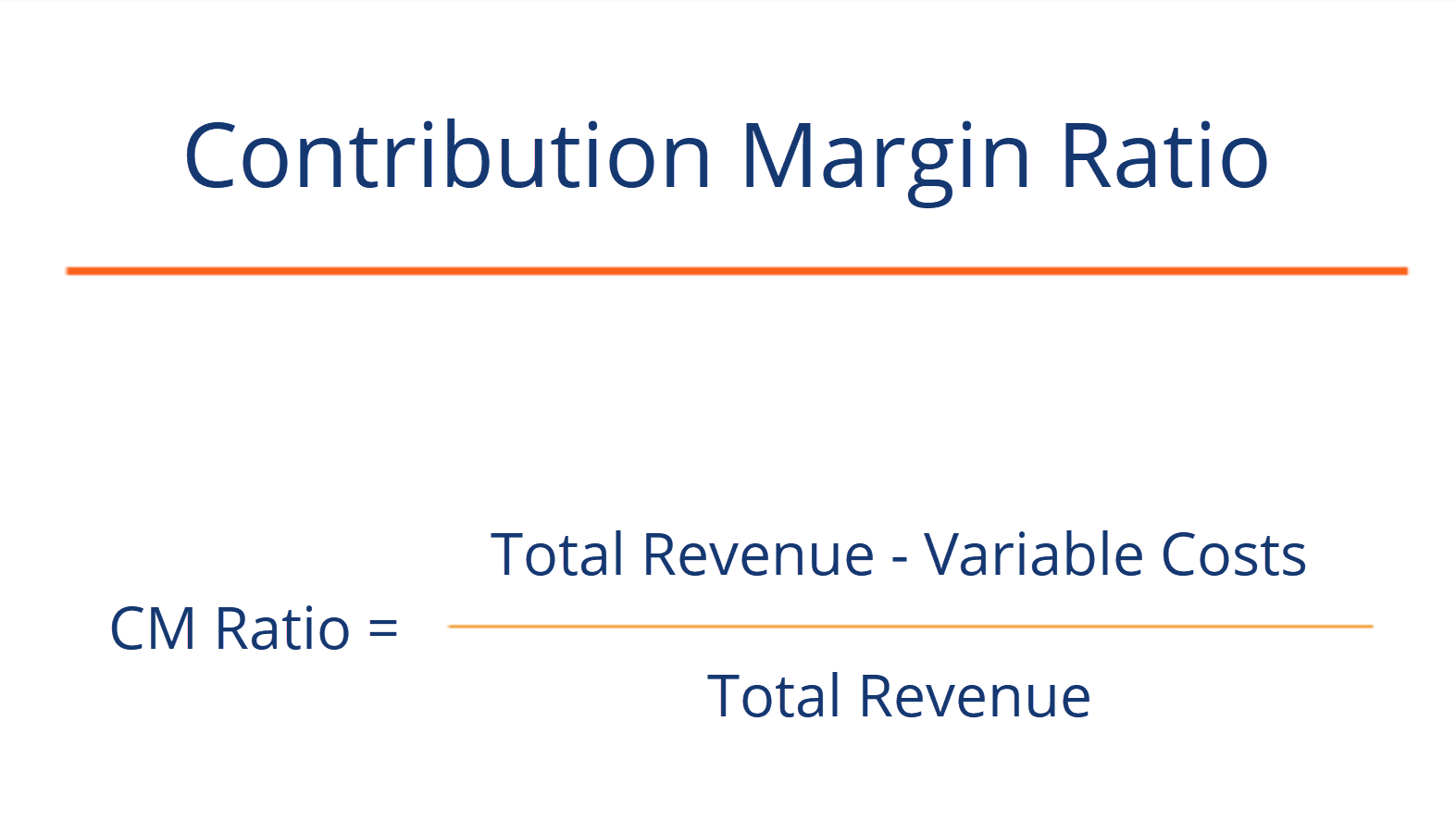
Furthermore, this ratio is also useful in determining the pricing of your products and the impact on profits due to change in sales. Accordingly, in the Dobson Books Company example, the contribution margin ratio was as follows. Thus, the contribution margin ratio expresses the relationship between the change in your sales volume and profit.
Contribution Margin Formula Components
- Keep in mind that contribution margin per sale first contributes to meeting fixed costs and then to profit.
- Gross margin is shown on the income statement as revenues minus cost of goods sold (COGS), which includes both variable and allocated fixed overhead costs.
- While there are plenty of profitability metrics—ranging from the gross margin down to the net profit margin—the contribution margin metric stands out for the analysis of a specific product or service.
- Thus, CM is the variable expense plus profit which will incur if any activity takes place over and above BEP.
Typical variable costs include direct material costs, production labor costs, shipping supplies, and sales commissions. Fixed costs include periodic fixed expenses for facilities rent, equipment leases, insurance, utilities, general & administrative (G&A) expenses, research & development (R&D), and depreciation of equipment. The key component of the contribution per unit calculation that can cause difficulty is the variable cost. This should only include those costs that vary directly with revenues. Thus, it should not include any overhead cost, and should rarely include direct labor costs. Direct labor costs are actually a fixed cost when a production line is used, since it requires a certain fixed amount of staffing to operate the line, irrespective of the number of units produced.
In fact, we can create a specialized income statement called a contribution margin income statement to determine how changes in sales volume impact the bottom line. If you need to estimate how much of your business’s revenues will be available to cover the fixed expenses after dealing with the variable costs, this calculator is the perfect tool for you. You can use it to learn how to calculate contribution margin, provided you know the selling price per unit, the variable cost per unit, and the number of units you produce. The calculator will not only calculate the margin itself but will also return the contribution margin ratio. For the month of April, sales from the Blue Jay Model contributed \(\$36,000\) toward fixed costs. The contribution margin is important because it helps your business determine whether selling prices at least cover variable costs that change depending on the activity level.
Accordingly, the per-unit cost of manufacturing a single packet of bread consisting of 10 pieces each would be as follows. 11 Financial is a registered investment adviser located in Lufkin, Texas. 11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements. 11 Financial’s website is limited to the dissemination of general information pertaining to its advisory services, together with access to additional investment-related information, publications, and links. Aside from the uses listed above, the contribution margin’s importance also lies in the fact that it is one of the building blocks of break-even analysis.
As you can see, the net profit has increased from $1.50 to $6.50 when the packets sold increased from 1000 to 2000. However, the contribution margin for selling 2000 packets of whole wheat what is pr payment what is pr payment by hatellove6294 bread would be as follows. Remember, that the contribution margin remains unchanged on a per-unit basis. Whereas, your net profit may change with the change in the level of output.
The contribution margin ratio is also known as the profit volume ratio. This is because it indicates the rate of profitability of your business. The gross sales revenue refers to the total amount your business realizes from the sale of goods or services.
It provides one way to show the profit potential of a particular product offered by a company and shows the portion of sales that helps to cover the company’s fixed costs. Any remaining revenue left after covering fixed costs is the profit generated. Overall, per unit contribution margin provides valuable information when used with other parameters in making major business decisions.
Investors examine contribution margins to determine if a company is using its revenue effectively. A high contribution margin indicates that a company tends to bring in more money than it spends. Fixed costs are often considered sunk costs that once spent cannot be recovered. These cost components should not be considered while making decisions about cost analysis or profitability measures. Now that we understand the basics, formula, and how to calculate per unit contribution margin, let us also understand the practicality of the concept through the examples below.
Now, let’s try to understand the contribution margin per unit with the help of an example. Variable Costs depend on the amount of production that your business generates. Accordingly, these costs increase with the increase in the level of your production and vice-versa. This means the higher the contribution, the more is the increase in profit or reduction of loss. In other words, your contribution margin increases with the sale of each of your products.
